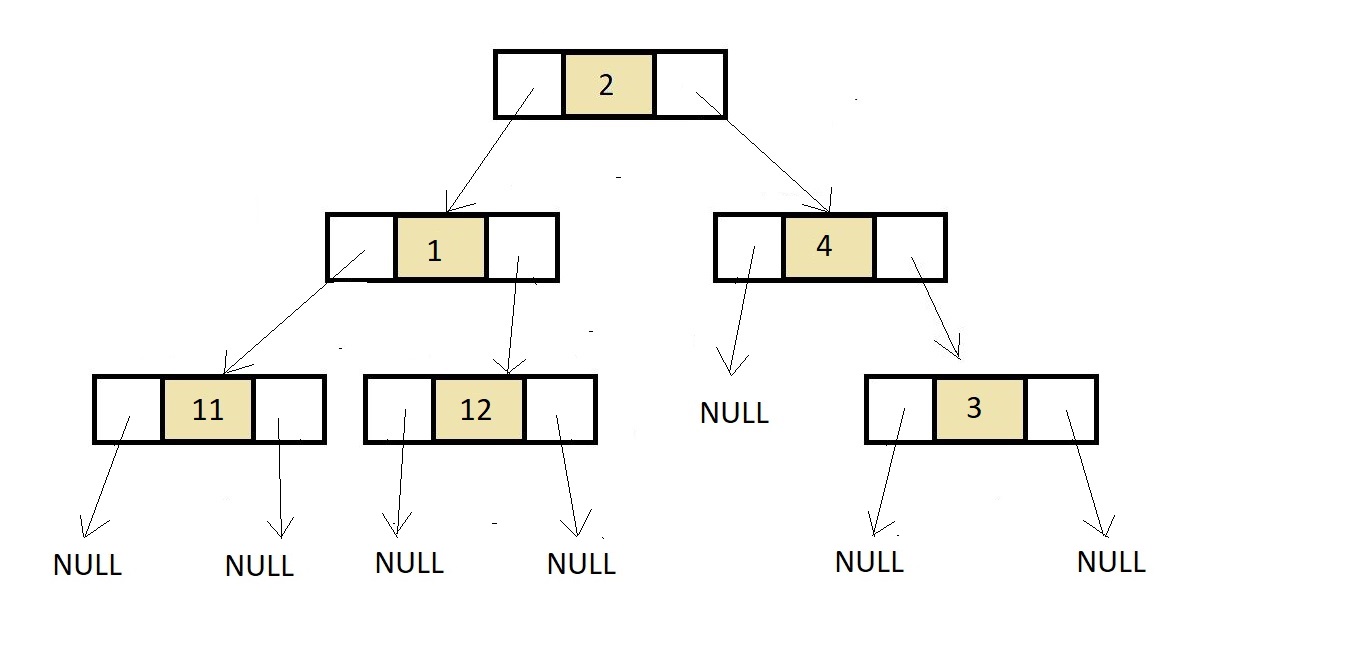
Linked Representation of Binary Tree
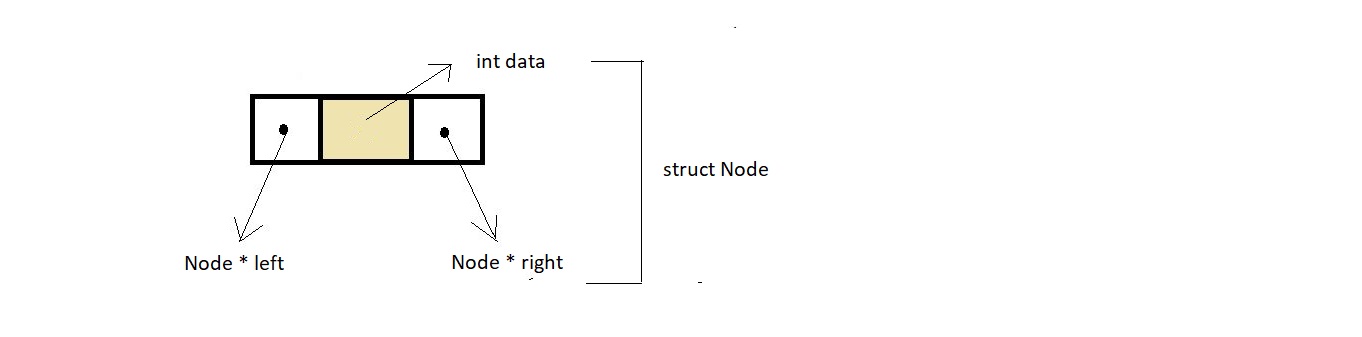
struct node {
int data;
struct node* left;
struct node* right;
};
struct node* CreateNode(int data){
struct node *n;
n = (struct node*)malloc(sizeof(struct node);
n->data = data;
n->left = NULL;
n->right = NULL;
return n;
}
struct node *p = createNode(2);
struct node *p1 = createNode(1);
struct node *p2 = createNode(4);
// Linking the root node with left and right children
p->left = p1;
p->right = p2;
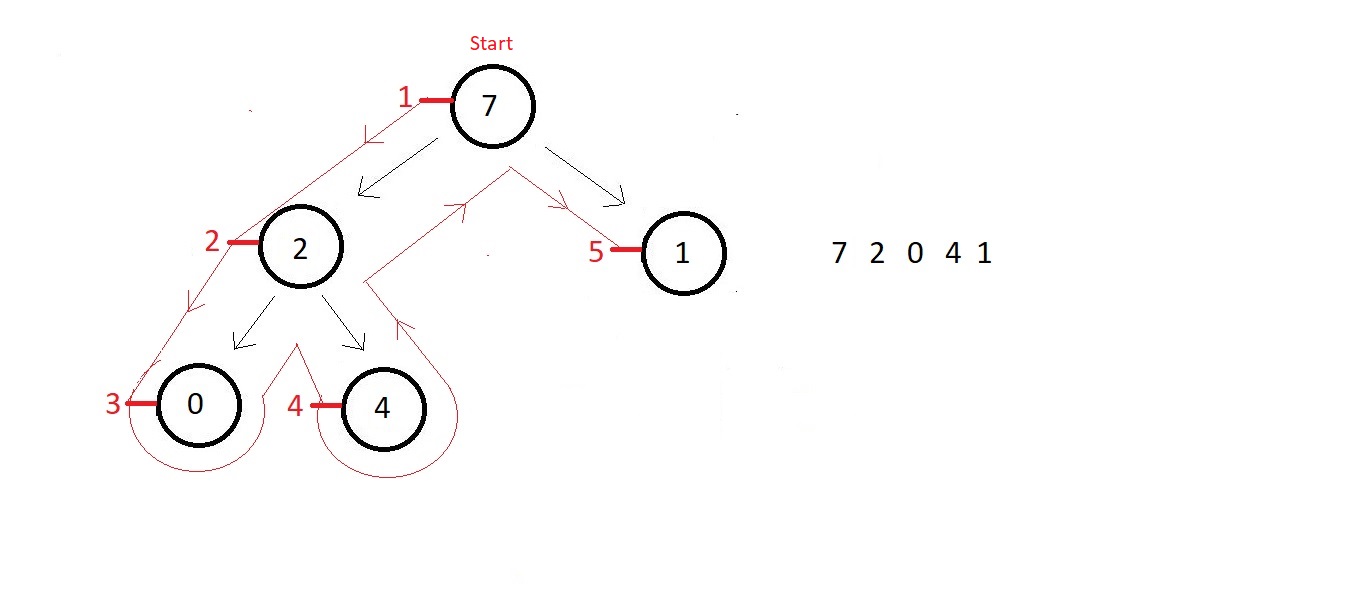
PreOrder traversal in Binary Tree
// Constructing the root node - Using Function (Recommended)
struct node *p = createNode(4);
struct node *p1 = createNode(1);
struct node *p2 = createNode(6);
struct node *p3 = createNode(5);
struct node *p4 = createNode(2);
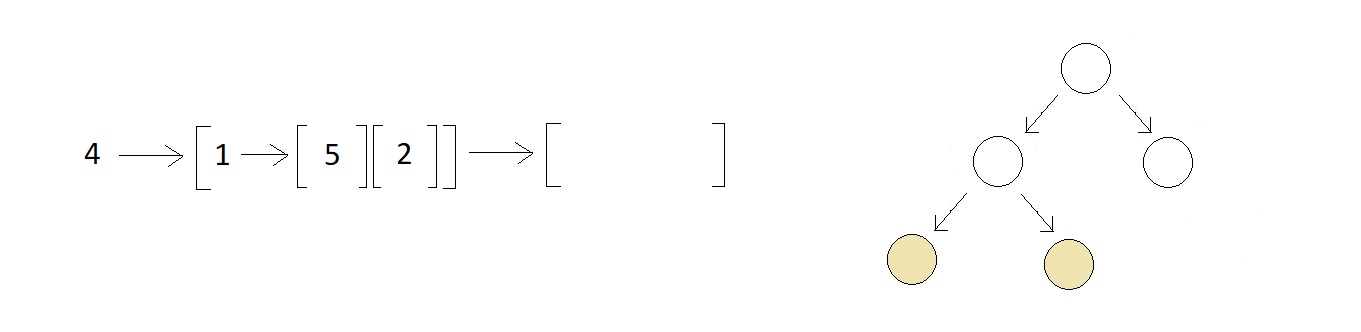
// Finally The tree looks like this:
// 4
// / \\
// 1 6
// / \\
// 5 2
// Linking the root node with left and right children
p->left = p1;
p->right = p2;
p1->left = p3;
p1->right = p4;
void preOrder(struct node* root){
if(root!=NULL){
printf("%d ", root->data);
preOrder(root->left);
preOrder(root->right);
}
}
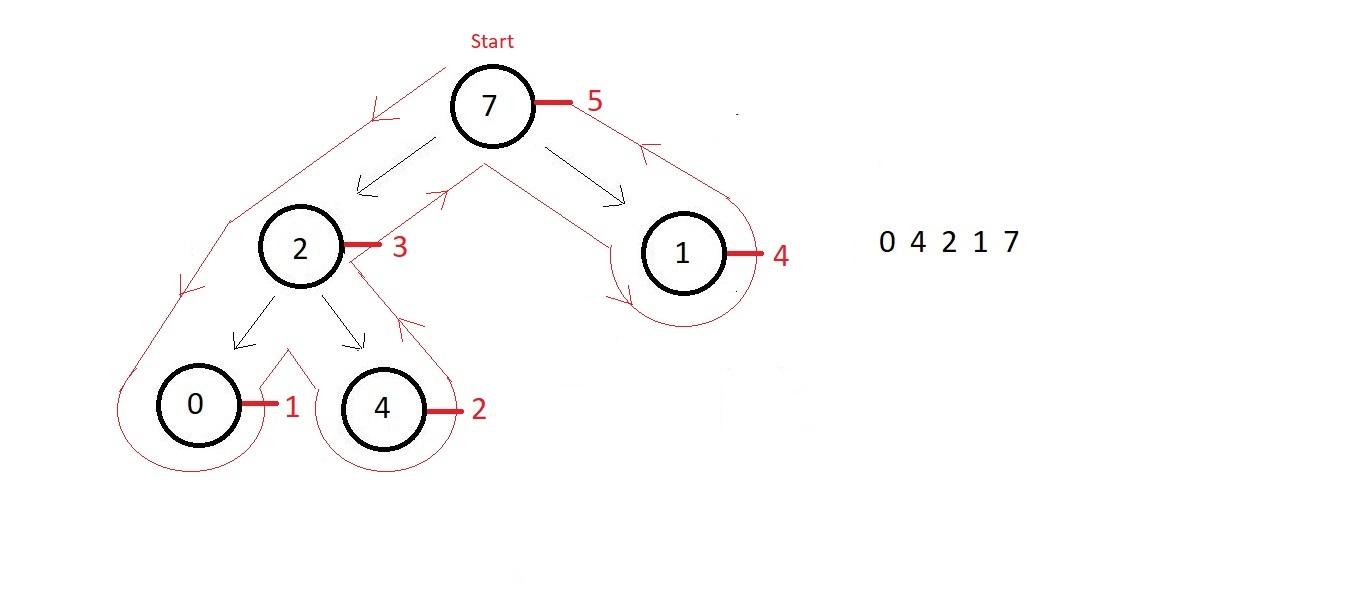
PostOrder traversal in binary tree
// Constructing the root node - Using Function (Recommended)
struct node *p = createNode(4);
struct node *p1 = createNode(1);
struct node *p2 = createNode(6);
struct node *p3 = createNode(5);
struct node *p4 = createNode(2);
// Finally The tree looks like this:
// 4
// / \\
// 1 6
// / \\
// 5 2
// Linking the root node with left and right children
p->left = p1;
p->right = p2;
p1->left = p3;
p1->right = p4;
void postOrder(struct node* root){
if(root!=NULL){
postOrder(root->left);
postOrder(root->right);
printf("%d ", root->data);
}
}








